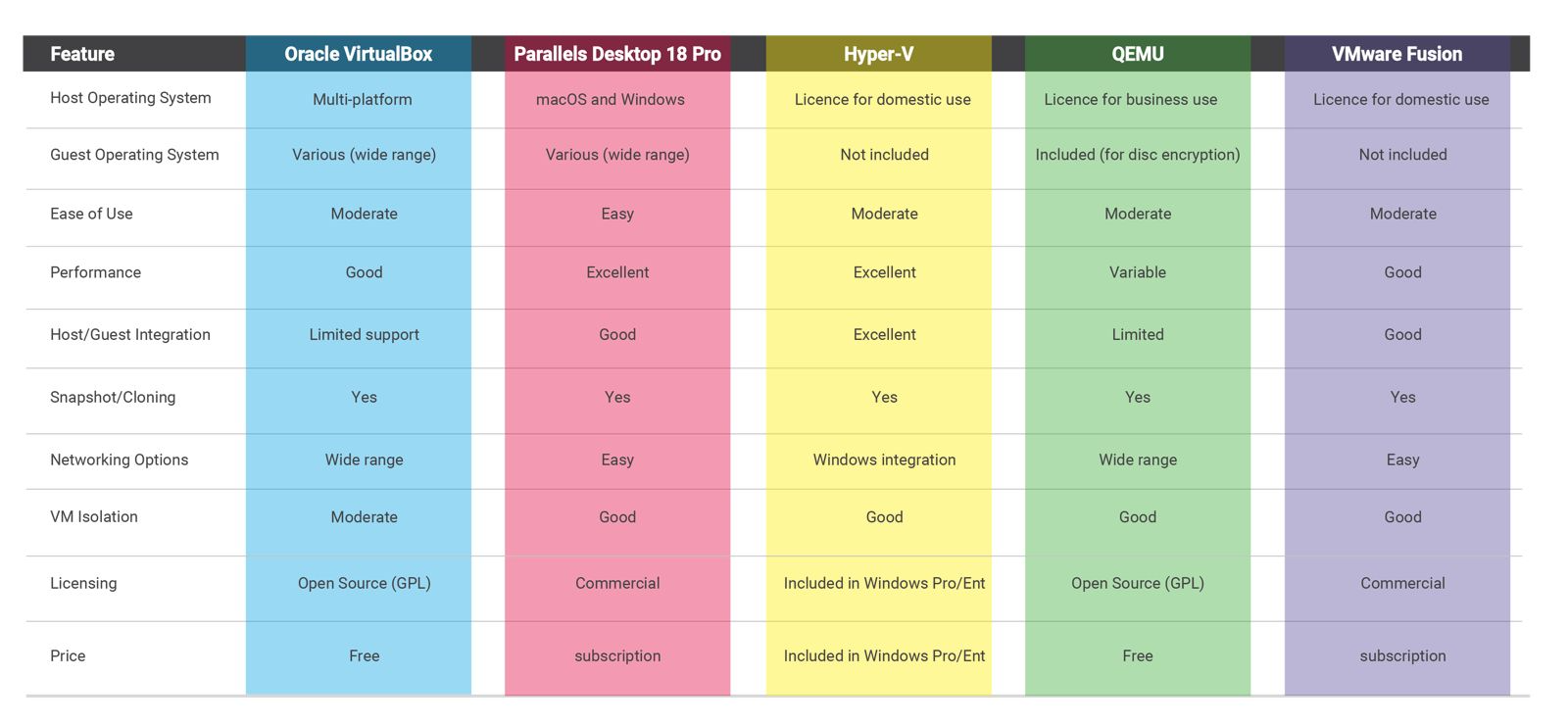
In this article, we provide a brief review of the virtual machines business state of art, and compare the most commonly used virtual machines like Virtualbox Oracle, Parallels Desktop, VMware Fusion, Hyper-V, and Qemu.

Virtual machines are virtualised environments that allow one or more operating systems to run within a host operating system, thus on one machine, PC or computer.
This solution offers many advantages, including isolation of systems, flexibility in running different platforms, and efficiency in the use of hardware resources, as well as the ability to run software that is not compatible with an operating system without having to purchase a different device or upgrade the one in use.
There are a variety of software options available on the market, each with its own strengths, features, and functionality; users are spoiled for choice depending on their needs.
Among the most popular ones, it is important to mention VirtualBox by Oracle, Parallels Desktop, VMware Fusion, Hyper-V, and QEMU.
Virtualbox by Oracle
VirtualBox is currently one of the most popular virtualization software packages, widely used to create and manage virtual machines on a variety of operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and others.
It has the distinction of being cross-platform, meaning that it can also be installed on operating systems other than macOS (e.g., Windows, Linux, and some versions of Solaris).
Compared with its rivals, it has a somewhat more complex structure, but it is still intuitive enough to install and use operating systems without particular problems.
Being open source, i.e., available to the community for free, it has limitations on some features and particularities; among the most interesting functions are the possibility of configuring different network modes for the virtual machine in use and folder sharing between the two working environments.
Parallels desktop
Parallels desktop is the flagship paid virtualization software from Parallels, Inc., designed specifically for macOS systems, enabling users to run Windows and Linux operating systems within their Mac.
It is known for its deep integration with macOS and its ability to run Windows smoothly on a Mac computer.
Parallels desktop is a popular choice among Mac users who need to run Windows applications or software on a macOS environment without the need to reboot the computer. It is known for its stability and ease of use and is widely used in professional and home environments.
Notable built-in features certainly include Coherence Mode, which allows you to hide the Windows interface and run Windows applications directly from the macOS dock (as if they were native applications), file and folder sharing between work environments, and graphics acceleration, which allows applications to run more smoothly.
Parallels desktop also allows the network to be configured to establish a direct connection to local networks and offers advanced development tools, for developers who need to test applications on different platforms.
Parallels Desktop 18 is available in two versions, the Standard and the Pro, with some major differences between the features included in each version.
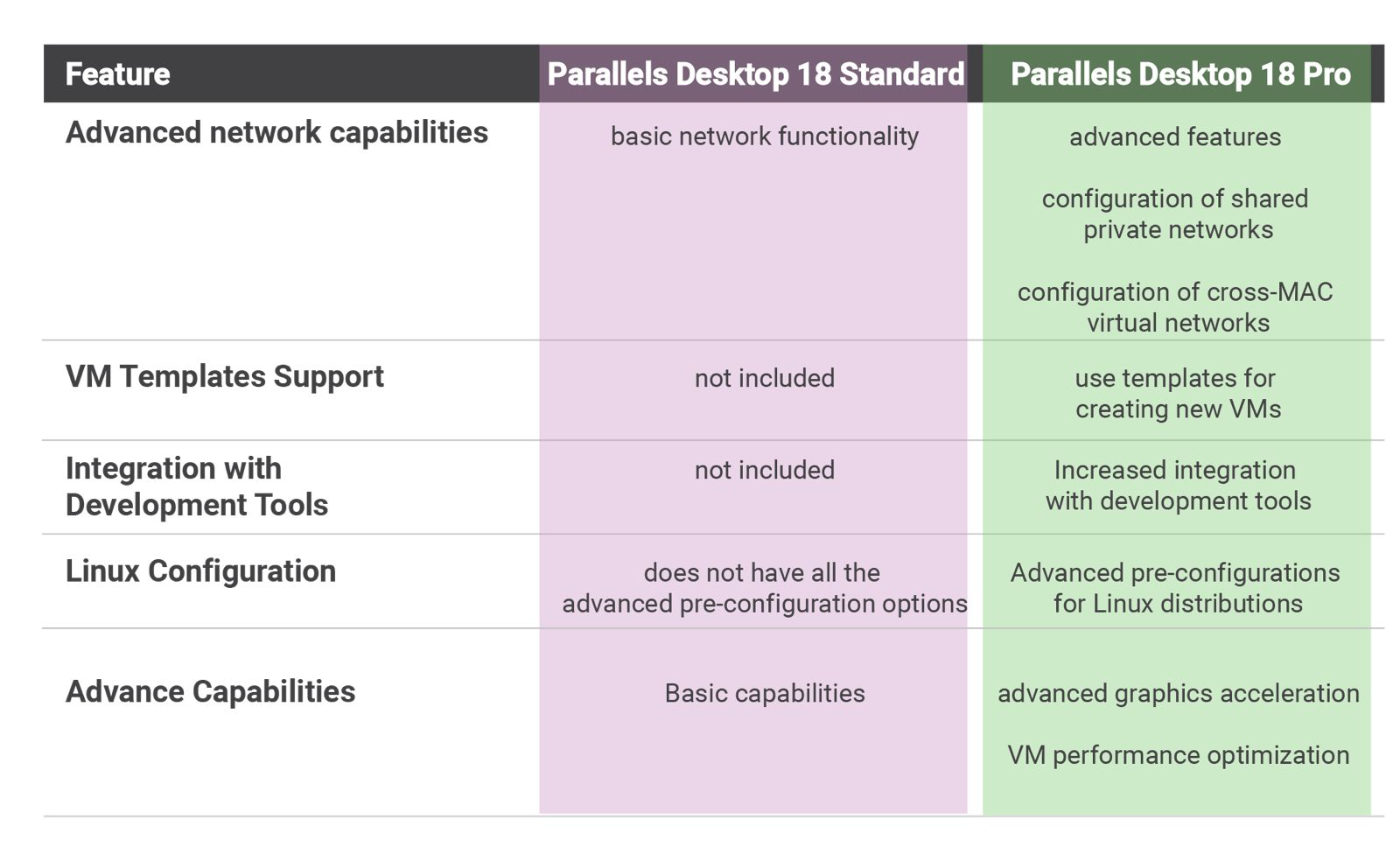
The choice strictly depends on the needs: for having advanced networking features or development tools, the Pro option is the best choice, while for a simpler and more straightforward working environment, a Standard edition is perfectly adequate.
Vmware Fusion
VMware Fusion software is designed specifically for macOS systems, enabling virtualization on Macs of Windows operating systems.
This software offers support for a wide range of guest operating systems, including different versions of Windows, Linux, macOS, and others. This allows users to use a wide variety of applications and software on different platforms.
VMware Fusion software allows Mac users to create and manage virtual machines for Linux as well.
Like Parallels, it features a Coherence mode, which hides the Windows interface providing a seamless experience, folder and file sharing, and advanced graphics acceleration to run programs with intensive graphics.
Vmware Workstation Pro 17
VMware Workstation Pro 17 stands as a pinnacle in virtualization technology, offering flexibility and performance for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
With its latest iteration, VMware provides robust platform for running multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single PC.
This software caters to a wide range of users, from developers needing diverse testing environments to IT administrators managing complex network configurations.
Noteworthy features include enhanced container integration, improved DirectX 11 and OpenGL 4.1 support for enhanced graphics performance, and advanced networking capabilities.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V is a virtualization technology developed by Microsoft that allows users to create and manage virtual machines on Windows systems.
As a necessary preamble, the software can be used only after Boot Camp is installed; this is an option for both macOS and Windows installed as a ‘guest’ on your machine.
Hyper-V is used primarily on Windows servers to implement server virtualization and provide virtualized data center services; it is a powerful and efficient virtualization solution, particularly suitable for users working primarily on Windows platforms.
It is widely used in enterprise environments for virtualizing servers and data center infrastructure, but can also be used on Windows desktop computers for development, testing, and local virtualization purposes.
Among its strengths, Hyper-V runs directly on the physical hardware of the native server or host computer, which allows for high performance; like most competitors, it supports a wide range of guest operating systems, including several types of Windows, Linux, and other operating systems, and is integrated with the Windows operating system, making it easy for those who work primarily using this operating system to configure and manage virtual machines.
In addition, Hyper-V allows management of virtual machines and related resources remotely.
Qemu
Like VirtualBox by Oracle, QEMU (Quick Emulator) is an open-source virtualization software that allows virtual machines to run on a variety of operating systems, including Linux, macOS, and Windows.
It is known for its flexibility and versatility, as it supports a wide range of hardware architectures and guest operating systems.
QEMU can be used for both emulation and virtualization and supports a wide range of hardware architectures and operating systems, making it useful for testing software on different platforms.
Because it is open-source software, it can be run on a wide variety of platforms and customized to your needs QEMU is a popular choice for developers and advanced users who want a highly flexible and customizable virtualization option.
However, due to its command-line-based nature and complexity, it may not be the best choice for less experienced users or for enterprise environments that require a graphical user interface and advanced management features.
Conclusions
Navigating the virtual machine business and choosing the right software can be challenging due to the variety of options available.
To assist in the selection process, we have summarized the main features of the software compared in this post in a table; we also offer a range of the products listed in this article on our site.